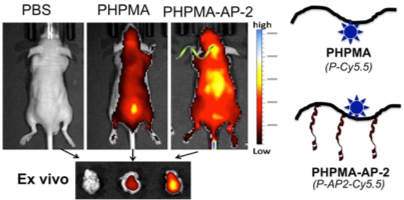
Nanomedicines designed for brain delivery/action have a difficult hurdle to overcome; they need to cross the blood brain barrier. We focus on receptor binding peptides that transcytose bound cargo into the brain. In particular, angiopep-2 (AP-2; TFFYGGSRGKRNNFKTEEY) binds to LDLR (low-density lipoprotein receptor)-related protein(LRP)-1 followed by transcytosis [1]. In collaboration with the Cedar-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and the University of Utah Department of Radiology we are developing conjugates suitable for the treatment of central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) and traumatic brain injury (TBI).
PCNSL is an aggressive CNS neoplasm with poor response to treatment, partially due to insufficient drug delivery efficiency across blood-brain-barrier (BBB). We developed a novel therapy for PCNSL by combining a targeted nano-polymer therapy with an immune checkpoint inhibitor (anti-PD1). HPMA copolymer based nanoconjugate (P-AP2-H6-cMyc AON) was designed to block c-Myc expression via anti-sense oligonucleotide (AON). Angiopep-2 peptide was conjugated to the polymer to facilitate the conjugate to cross the BBB. The systemically administered polymer conjugate alone or in combination with anti-PD1 antibody was active in the treatment of syngeneic orthotopic mouse model of intracranial brain lymphoma (Figure 2).